Fetal movements are one of the most reassuring signs for expectant mothers, indicating that the baby is developing well inside the womb. These movements, often called “kicks,” are a form of communication between the mother and the unborn child, signaling their health and vitality. Tracking and interpreting these movements is crucial for monitoring the baby’s well-being throughout pregnancy. This article will guide you through the process of tracking fetal movements, understanding what is normal, and when to seek medical advice.
Exploring Fetal Movements
Fetal movements are a fascinating and reassuring aspect of pregnancy, offering the first real connection between mother and child. These movements, which start as gentle flutters and progress to more pronounced kicks and rolls, are a key indicator of your baby’s health and development. Understanding and exploring these movements can help you bond with your baby while providing important information about their well-being.
Why Do Babies Move and When It Begins?
Fetal movements are a natural part of your baby’s development. They start as spontaneous muscle twitches as the nervous system begins to mature. Over time, these movements become more purposeful, such as stretching, turning, and hiccupping. Movement helps your baby’s bones and muscles grow stronger and also plays a role in brain development.
Fetal movements typically begin to be noticeable between 18 and 24 weeks of pregnancy, though some mothers may feel them earlier, especially in subsequent pregnancies. Many women ask what is the quickening in pregnancy? These early movements, often called “quickening,” may feel like tiny flutters, bubbles, or even gentle taps. Below, we’ll learn more about quickening types.
Types of Fetal Movements
As your baby grows, the nature of their movements will change.
- Flutters and Quickening: In the early stages, movements may be so gentle that you might mistake them for gas or digestive activity. These flutters are your baby’s early attempts at movement.
- Kicks and Punches: As your baby’s muscles strengthen, the movements will become more pronounced. You’ll feel distinct kicks, jabs, and punches, especially when your baby stretches their arms and legs.
- Rolling and Turning: By the third trimester, your baby may begin to roll or turn, which can feel like a wave or a shift inside your belly. These larger movements often occur when your baby is changing position.
- Hiccups: Hiccups are another common type of fetal movement, typically felt as rhythmic, repetitive jerks. Your baby’s developing diaphragm causes these as they practice breathing movements.
How to Track Fetal Movements
There are several methods to track fetal movements, and finding the one that works best for you is essential.
Kick Counts
The most common method is to count how long it takes to feel ten movements. Choose a time of day when your baby is usually active, and find a comfortable, quiet spot where you can focus. Typically, you should feel 10 movements within two hours, although it often takes much less time.
Daily Tracking
Some women prefer to track their baby’s movements at the same time every day, noting the number of kicks within a specific period, such as one hour.
Movement Chart
Using a chart or an app to record movements can help you spot patterns over time.
This can be particularly helpful in the later stages of pregnancy when tracking movements becomes a regular part of your routine.
Interpreting Fetal Movements
Understanding what is normal for your baby is key to interpreting fetal movements. While some babies are naturally more active, others might have quieter days. Learning your baby’s routine and being aware of any significant changes is important.
Variations in Movement
It’s normal for the type and intensity of movements to change as your baby grows. Early in pregnancy, movements may feel like flutters, but by the third trimester, they may become stronger, resembling kicks and rolls.
Position Changes
As your baby changes position, you might notice a temporary movement decrease. For example, if your baby turns to face your spine, their movements may feel less pronounced.
Times of Activity
Many babies are more active at certain times of the day, often in the evening or after you’ve eaten. Knowing these patterns will help you recognize what is normal for your baby.
When to Seek Medical Advice
While variations in movement are usually normal, a sudden decrease in fetal movements could be a sign of a problem. You should contact your healthcare provider if:
- You notice a significant reduction in your baby’s movements.
- You do not feel 10 movements within two hours.
- There is a sudden, severe change in the type of movements.
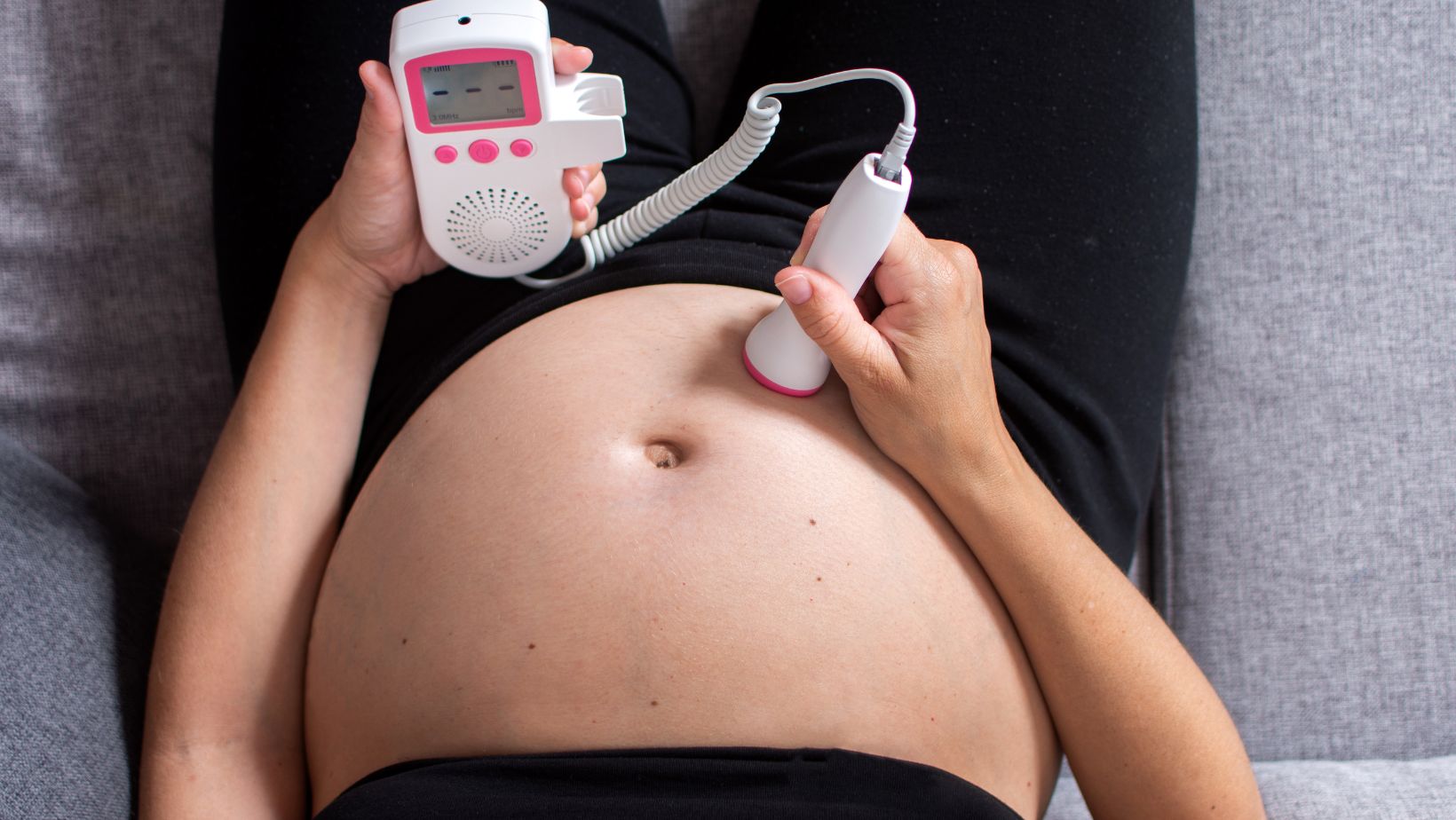
Your healthcare provider may suggest additional monitoring, such as a non-stress test or an ultrasound, to ensure your baby is healthy.
The Bottom Line
Tracking and interpreting fetal movements is a crucial aspect of prenatal care. Paying close attention to your baby’s movements can gain valuable insight into their well-being and ensure that any potential issues are addressed promptly. Remember, you know your body and baby best, so trust your instincts and don’t hesitate to seek medical advice if you have any concerns.
